MULTI-THREADING
Thread is the smallest unit of execution within a process. Threads within the same process share memory and resources, facilitating communication and data sharing. Multi-threading is the ability of a program or an operating system to enable more than one user at a time without requiring multiple copies of the program running on the computer.
Creating a thread is less expensive than creating a new process because the newly created thread uses the current process address space.
Concurrency: Multiple threads are making progress at the same time. This is more about dealing with multiple tasks at once rather than running them simultaneously.
Non-blocking Operations: Threads enable non-blocking I/O operations, where one thread can handle input/output operations while other threads continue executing without waiting.
Faster Response Times: With the ability to process multiple requests concurrently, client requests can be handled more quickly, reducing the time each client waits for a response.
Handling High Loads: Concurrent servers can scale to handle a large number of simultaneous connections, making them suitable for high-traffic applications like web servers, email servers, and database servers.
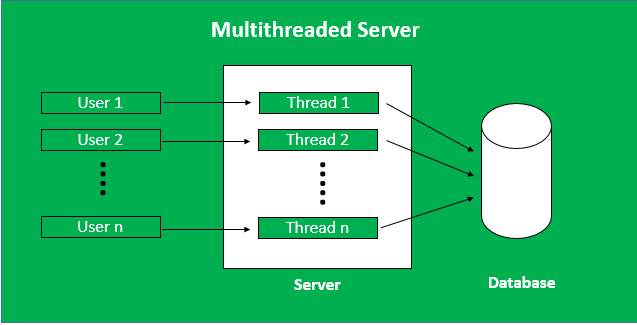
System calls used for managing threads
pthread_create() - create a new thread
int pthread_create(pthread_t * thread,
const pthread_attr_t * attr,
void * (*start_routine)(void *),
void *arg);- thread: pointer to an unsigned integer value that returns the thread id of the thread created.
- attr: pointer to a structure that is used to define thread attributes like detached state, scheduling policy, stack address, etc. Set to NULL for default thread attributes.
- start_routine: pointer to a subroutine that is executed by the thread. The return type and parameter type of the subroutine must be of type void *. The function has a single attribute but if multiple values need to be passed to the function, a struct must be used.
- arg: pointer to void that contains the arguments to the function defined in the earlier argument
pthread_exit() - terminate calling thread
void pthread_exit(void *retval);- retval: is the pointer to an integer that stores the return status of the thread terminated.The scope of this variable must be global so that any thread waiting to join this thread may read the return status.
pthread_detach() - detach a thread
int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread);- thread: thread id of the thread that must be detached.
Return value: on success, returns 0.If error occurs returns an error number